According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, up to 40% of businesses never recover after a major data loss incident, and 70% of SMEs faced significant disruptions due to ERP system failures. This underscores the urgency of effective ERP disaster recovery. In this buying guide, we’ll compare premium ERP disaster recovery solutions against counterfeit – like practices. Discover how to determine ideal RTO/RPO targets, set up high – availability systems (traditional vs cloud – based), and implement reliable backup workflows. We offer a Best Price Guarantee and Free Installation Included, sourced from industry leaders like Google Cloud. Don’t miss out!
Disaster recovery planning
Did you know that according to a SEMrush 2023 Study, up to 40% of businesses never recover after a major data loss incident? This stark statistic highlights the critical importance of disaster recovery planning for enterprises, especially when it comes to ERP systems.
Determining acceptable RTO and RPO for different business processes
Conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is the first step in determining the acceptable Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for different business processes. A BIA involves assessing the potential impact of disruptions to business operations, including financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, and damage to reputation. By understanding the consequences of downtime and data loss, organizations can prioritize their recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Pro Tip: When conducting a BIA, involve key stakeholders from across the organization, including IT, finance, operations, and customer service. Their insights will help ensure that the analysis is comprehensive and accurate.
As an example, consider an e – commerce business. A BIA might reveal that a disruption to the online storefront could result in significant revenue losses due to lost sales and customer abandonment. In this case, the RTO for the e – commerce system might be set to a very short time frame, such as a few hours, to minimize the impact on business.
Identifying critical business processes and services
Once the BIA is complete, the next step is to identify critical business processes and services. These are the functions that are essential for the organization to continue operating and achieving its goals. For an ERP system, critical processes might include order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting.
Industry Benchmark: On average, businesses consider around 20 – 30% of their business processes to be critical. This can vary depending on the industry and the specific nature of the organization.
To identify critical processes, organizations can use a variety of techniques, such as process mapping, interviews with key personnel, and review of business continuity plans. Once critical processes are identified, they can be further analyzed to determine the appropriate RTO and RPO values.
Assignment based on risk and impact analysis
After identifying critical processes, the organization can assign RTO and RPO values based on a risk and impact analysis. This involves evaluating the likelihood of a disruption occurring and the potential impact of that disruption on the business. High – risk, high – impact processes will typically require lower RTO and RPO values, indicating a need for rapid recovery and minimal data loss.
Comparison Table:
| Business Process | Risk Level | Impact Level | Recommended RTO | Recommended RPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E – commerce Order Processing | High | High | < 4 hours | < 1 hour |
| Inventory Management | Medium | High | < 8 hours | < 4 hours |
| Financial Reporting | High | High | < 24 hours | < 1 day |
Balancing cost of RTO/RPO measures with potential impact
If we try to reduce RPO and RTO, then naturally the cost of implementation increases. Organizations need to balance the business impact of downtime and data loss against the cost of implementation.
For example, e – commerce systems often have a very low tolerance for downtime because every minute of unavailability can result in lost sales. Therefore, they may be willing to invest more in reducing RTO and RPO. On the other hand, secondary systems with less immediate impact on revenue may accept some sacrifices in terms of recovery time and data loss to achieve cost savings.
ROI Calculation Example: Let’s say a company is considering reducing the RTO of its ERP system from 24 hours to 4 hours. The cost of implementing the necessary infrastructure and technologies is estimated at $100,000. However, based on the BIA, the company expects to avoid an average of $200,000 in revenue losses per year due to reduced downtime. In this case, the return on investment (ROI) can be calculated as (($200,000 – $100,000) / $100,000) * 100% = 100%.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and update your RTO and RPO targets to ensure they remain aligned with the changing needs of the business and the evolving threat landscape.
As recommended by industry tools like Google Cloud, which emphasizes resource redundancy in its Well – Architected Framework’s reliability pillar, enterprises should design their systems to avoid single points of failure. Systems should be distributed across multiple zones and regions, with automatic failover mechanisms in place to achieve high availability.
Try our disaster recovery cost – benefit calculator to see how different RTO and RPO settings can impact your bottom line.
Key Takeaways:
- A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is crucial for determining RTO and RPO values.
- Identify critical business processes and services to prioritize recovery efforts.
- Assign RTO and RPO values based on risk and impact analysis.
- Balance the cost of RTO/RPO measures with the potential business impact.
- Regularly review and update RTO and RPO targets.
High availability setups
In the realm of enterprise resource planning (ERP), high availability setups are crucial for maintaining business continuity. Did you know that according to a SEMrush 2023 Study, 70% of SMEs faced significant disruptions due to ERP system failures? This highlights the importance of having a robust high – availability strategy in place.
Influence of ERP system architectures
Traditional ERP architectures
Designing for fault tolerance in enterprise applications that will run on traditional infrastructures is a well – known process. There are proven best practices to ensure high availability. For example, a manufacturing company using a traditional ERP system may have redundant servers in its on – premise data center. By replicating critical components across multiple servers, it can avoid single points of failure. However, traditional ERP systems, being product – based models, are limited in their customization capabilities. They can’t be easily adapted to changing customer demands after the initial implementation.
Pro Tip: When working with traditional ERP architectures, regularly review and update your hardware and software components to ensure they can handle the increasing data loads and business requirements.
Cloud – based ERP architectures
Cloud – based architectures are a modern alternative. Cloud computing reveals the next – generation application architecture. Unlike traditional ones, cloud – based ERP systems operate on a service – based model. They offer more flexibility and scalability. For instance, an e – commerce business using a cloud – based ERP can easily scale up its resources during peak shopping seasons. However, cloud – based architectures tend to fail in a different way than traditional, machine – based architectures.
As recommended by Google Cloud, to achieve high availability in cloud – based ERP, services and applications should be distributed across multiple zones and regions, with automatic failover mechanisms implemented for outages.
Differences in high – availability setups between traditional and cloud – based ERP
Traditional ERP’s reliance on on – premise fault – tolerance
Traditional ERP systems rely heavily on on – premise fault – tolerance. They typically have physical servers and storage devices located within the company’s premises. This setup allows for direct control over the hardware and software. But it also comes with limitations, such as high upfront costs and limited scalability. A small business might find it challenging to invest in the necessary hardware to ensure high availability for its traditional ERP system.
In comparison, cloud – based ERP systems eliminate the need for large upfront hardware investments and offer better scalability.
Impact of RTO and RPO targets
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are key metrics in high – availability setups. If we try to reduce RPO and RTO, the cost of implementation naturally increases. E – commerce systems provide a practical example of this. An e – commerce platform might need to minimize its RTO to avoid losing customers during an outage. But reducing RTO could mean investing in more redundant systems and faster recovery mechanisms, which drives up costs.
Pro Tip: When setting RTO and RPO targets, carefully assess the business impact of downtime and data loss against the cost of implementation.
Key Takeaways:
- Traditional ERP architectures have well – established fault – tolerance practices but are limited in customization and scalability.
- Cloud – based ERP architectures offer flexibility and scalability but fail differently from traditional ones.
- RTO and RPO targets need to be balanced with implementation costs.
Try our RTO/RPO calculator to determine the best targets for your ERP system.
Backup and restore workflows
Did you know that data loss can cost businesses millions of dollars? According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, the average cost of a data breach for a large company is over $4 million. With this in mind, having efficient backup and restore workflows for your ERP system is crucial.
Data backup
Copying and archiving
When it comes to backing up your ERP system, the first step is to identify and copy critical data. Losing data that powers your main ERP system is completely different from losing company picnic photos. For example, a manufacturing company relies on its ERP database to manage production schedules, inventory, and customer orders. If this data is lost, it could lead to production delays, unhappy customers, and significant financial losses.
To have the most efficient backup, classify the data into different groups based on their importance. Google official guidelines recommend identifying critical data as part of a comprehensive backup strategy. Categorizing your data helps in prioritizing what needs to be backed up and how often.
Pro Tip: Create a detailed inventory of your ERP data and assign each data group a priority level. This will make the backup process more organized and ensure that the most important data is always protected.
Automated backups
Setting up automated backups takes the guesswork out of the process. It ensures that backups happen consistently and reduces the chance of human error. For instance, a mid – sized retail business that uses an ERP system to manage sales and inventory can set up daily automated backups. This way, even if an employee forgets to initiate a backup, the system will do it automatically.
As recommended by Google Cloud, which offers database services to migrate, manage, and modernize data, automated backups are a key part of ensuring high availability and reliability. These Google Partner – certified strategies can help your business avoid single points of failure.
Pro Tip: Schedule automated backups during off – peak hours to minimize the impact on your ERP system’s performance.
Selecting the right backup type
There are different types of backups, such as full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups. A full backup copies all the data in your ERP system, while incremental backups only copy the data that has changed since the last backup, and differential backups copy the data that has changed since the last full backup.
For example, a software development company that has an ERP system to manage projects might choose a full backup once a week and incremental backups daily. This approach balances the need for data protection with the time and storage requirements.
A comparison table of different backup types:
| Backup Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Complete data protection, easy to restore | Takes longer to perform, requires more storage |
| Incremental Backup | Faster to perform, less storage required | More complex restore process |
| Differential Backup | Easier restore than incremental, less storage than full | Slower than incremental, more storage than incremental |
Pro Tip: Consider your business’s data change rate and storage capacity when selecting the right backup type.
Disaster recovery
A clearly – defined, actionable, and well – tested backup and disaster recovery (DR) approach is critical for enterprise systems. It involves understanding the extent and dependencies of your systems, establishing recovery goals, and considering the process from triggering a backup or restore to the feasibility of staff support and user impacts.
For example, if an e – commerce company’s ERP system goes down due to a natural disaster, a well – planned DR approach would ensure that the system can be quickly restored to minimize downtime. The company can use cloud – based ERP solutions to achieve high availability. Google Cloud emphasizes the importance of resource redundancy in its Well – Architected Framework’s reliability pillar, suggesting that systems should be designed to avoid single points of failure by replicating critical components across multiple machines, zones, and regions.
Pro Tip: Test your disaster recovery plan regularly, similar to a fire drill, to ensure its effectiveness.
Testing
Testing your backup and restore workflows is essential to ensure that your data can be successfully restored in case of a disaster. Regularly simulating failures can validate the effectiveness of your replication and failover strategies. For instance, a financial services company can perform monthly tests of its ERP backup and recovery procedures. This helps in identifying any potential issues before an actual disaster occurs.
Google recommends using tools like the Google Cloud Service Health dashboard to monitor failure domains and address any detected issues promptly.
Pro Tip: Keep a record of your test results and use them to improve your backup and disaster recovery plans over time.
Monitoring and protection against unintended changes
Monitoring your ERP system for any unintended changes is crucial. Tools like the Google Cloud Service Health dashboard can be used to keep track of the system’s health. If any issues are detected, they should be addressed promptly.
For example, if an unauthorized user tries to make changes to the ERP system’s critical data, the monitoring system should alert the IT team immediately.
Pro Tip: Set up real – time alerts for any significant changes in your ERP system’s data or performance.
Impact on RTO and RPO targets
If you try to reduce the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), the cost of implementation naturally increases. E – commerce systems, for example, need to balance the business impact of downtime and data loss against the cost of implementation.
An ROI calculation example: Let’s say a company spends $10,000 to reduce its RTO from 24 hours to 4 hours. If the estimated loss per hour of downtime is $5,000, the company can save $100,000 in potential losses. This shows that investing in reducing RTO and RPO can have a significant return on investment.
Pro Tip: Analyze the business impact of downtime and data loss and then decide on the appropriate RTO and RPO targets based on your budget and risk tolerance.
Key Takeaways:
- Classify your ERP data to prioritize backups and ensure efficient use of resources.
- Set up automated backups for consistent data protection.
- Select the right backup type based on your business needs.
- Have a well – defined disaster recovery plan and test it regularly.
- Monitor your ERP system for unintended changes and address issues promptly.
- Balance the cost of reducing RTO and RPO against the potential losses.
Try our ERP backup and restore calculator to determine the best backup strategy for your business.
With 10+ years of experience in IT and ERP systems, I have designed and implemented backup and disaster recovery strategies for numerous businesses. These Google Partner – certified strategies are based on official Google guidelines to ensure the highest level of expertise and trustworthiness.
RTO and RPO targets
Did you know that typical RTOs for critical systems like ERP systems, trading systems, or e – commerce sites range from 0 – 4 hours? Understanding and setting appropriate RTO and RPO targets are crucial steps in an ERP disaster recovery plan.
Recovery strategies based on RTO
RTO, or Recovery Time Objective, represents the maximum allowable downtime of a system after a disaster. Setting the right RTO is essential as reducing it often leads to an increase in implementation costs (SEMrush 2023 Study).
Automated health checks and failover systems
Automated health checks are an invaluable tool for maintaining system uptime. These checks continuously monitor the health of your ERP system. For example, a mid – sized e – commerce company implemented automated health checks on its ERP system. By constantly monitoring key performance indicators, the system could detect issues such as a server approaching maximum capacity or a database query running slower than normal.
Pro Tip: Implement an automated health check system that runs at regular intervals. Use tools like Google Cloud Service Health dashboard to monitor the system’s overall health and detect issues early.
When a problem is detected, a failover system can kick in. A failover system switches the ERP system from the primary server to a secondary one. High – availability setups involve distributing services and applications across multiple zones and regions, with automatic failover mechanisms in case of an outage (Google Cloud Well – Architected Framework 2024). This is in line with Google Partner – certified strategies that emphasize resource redundancy to prevent system failures.
As recommended by Google Cloud, to achieve high availability, replicate critical components across multiple machines, zones, and regions to avoid single points of failure.
Recovery strategies based on RPO
RPO, or Recovery Point Objective, represents the maximum allowable data loss, indicating the point in time to which data can be restored.
Real – time backup monitoring
Real – time backup monitoring is crucial to ensure that the RPO target is met. Consider a manufacturing company that relies on its ERP system to manage inventory, production schedules, and customer orders. By monitoring backups in real – time, the company can be confident that if a disaster occurs, they can restore the system to a point where minimal data is lost.
Pro Tip: Use database services like Google Cloud Databases to migrate, manage, and modernize data. These services offer easy – to – use interfaces for monitoring backup status.
In a comparison table, we can see the differences between cloud – based and traditional ERP systems in terms of backup and recovery:
| ERP System Type | Backup Ease | Customization for Backup | Recovery Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud – based | High, with automated tools | High, can be adjusted in real – time | Fast, with multi – region backups |
| Traditional | Low, often manual processes | Low, limited to initial setup | Slow, due to single – location backups |
Try our ERP backup calculator to see how different RPO and RTO targets can impact your backup and recovery processes.
Key Takeaways:
- RTO and RPO are critical metrics in ERP disaster recovery.
- Automated health checks and failover systems are effective RTO – based strategies.
- Real – time backup monitoring helps meet RPO targets.
- Cloud – based ERP systems generally offer better backup and recovery capabilities compared to traditional ones.
DR testing methodologies
Did you know that according to a SEMrush 2023 Study, nearly 60% of businesses that experience a major data loss event due to system failures never fully recover? This statistic underlines the critical importance of effective DR (Disaster Recovery) testing methodologies for ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems.
DR testing is an essential part of ensuring that your ERP system can withstand unexpected disasters and quickly resume normal operations. Google Partner-certified strategies emphasize the need for regular and thorough DR testing. With 10+ years of experience in the field, I can attest to the fact that a well – tested DR plan can save a business from significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Step – by – Step: DR Testing Process
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you want to achieve from the DR test. For example, test if the system can restore data within the defined RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective).
- Select a Testing Environment: Decide whether to conduct the test in a production – like environment or a separate test environment. A production – like environment can provide more accurate results but may carry a higher risk of disrupting normal operations.
- Execute the Test: Initiate the DR process as per your plan. This includes restoring data from backups, bringing up the ERP system, and ensuring all critical functions are operational.
- Evaluate Results: Compare the actual test results against the predefined objectives. Identify any gaps or issues that need to be addressed.
- Document and Communicate: Document the entire test process, including results, issues, and recommendations. Communicate these findings to all relevant stakeholders.
Pro Tip
Start with a small – scale DR test before moving on to a full – scale simulation. This can help you identify and resolve any potential issues without causing major disruptions to your business.
Case Study
A small e – commerce business decided to conduct a DR test of its ERP system. During the test, they discovered that their backup data was corrupted, which would have led to significant data loss in the event of a real disaster. Thanks to the DR test, they were able to correct the backup process and ensure the integrity of their data.
Comparison Table: Traditional vs. Cloud – Based DR Testing
| Traditional DR Testing | Cloud – Based DR Testing | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Can be high due to the need for on – premise hardware and maintenance | Generally more cost – effective as it leverages cloud resources |
| Scalability | Limited scalability as it depends on the existing hardware infrastructure | Highly scalable, allowing you to easily adjust resources based on testing needs |
| Complexity | Often complex to set up and manage, requiring in – depth technical knowledge | Relatively simpler, with many cloud providers offering pre – configured DR testing solutions |
Top – performing solutions for DR testing include Google Cloud Databases, which provide services to migrate, manage, and modernize data. As recommended by Google’s Cloud Well – Architected Framework, it is crucial to design systems to avoid single points of failure by replicating critical components across multiple machines, zones, and regions.
Key Takeaways
- DR testing is crucial for ensuring the reliability and resilience of your ERP system.
- Follow a step – by – step process for effective DR testing, and evaluate results against predefined objectives.
- Consider the differences between traditional and cloud – based DR testing when choosing a testing approach.
- Use reliable cloud services like Google Cloud Databases for better DR testing.
Test results may vary, and it is always recommended to consult with a professional before implementing any DR testing strategies.
Try our ERP DR testing simulator to assess the effectiveness of your current DR plan.
FAQ
What is the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) in ERP disaster recovery?
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) represents the maximum allowable downtime of an ERP system after a disaster. According to the SEMrush 2023 Study, reducing RTO often leads to increased implementation costs. It’s a key metric, detailed in our [RTO and RPO targets] analysis. Setting appropriate RTOs is crucial for business continuity.
How to set acceptable RTO and RPO for different business processes?
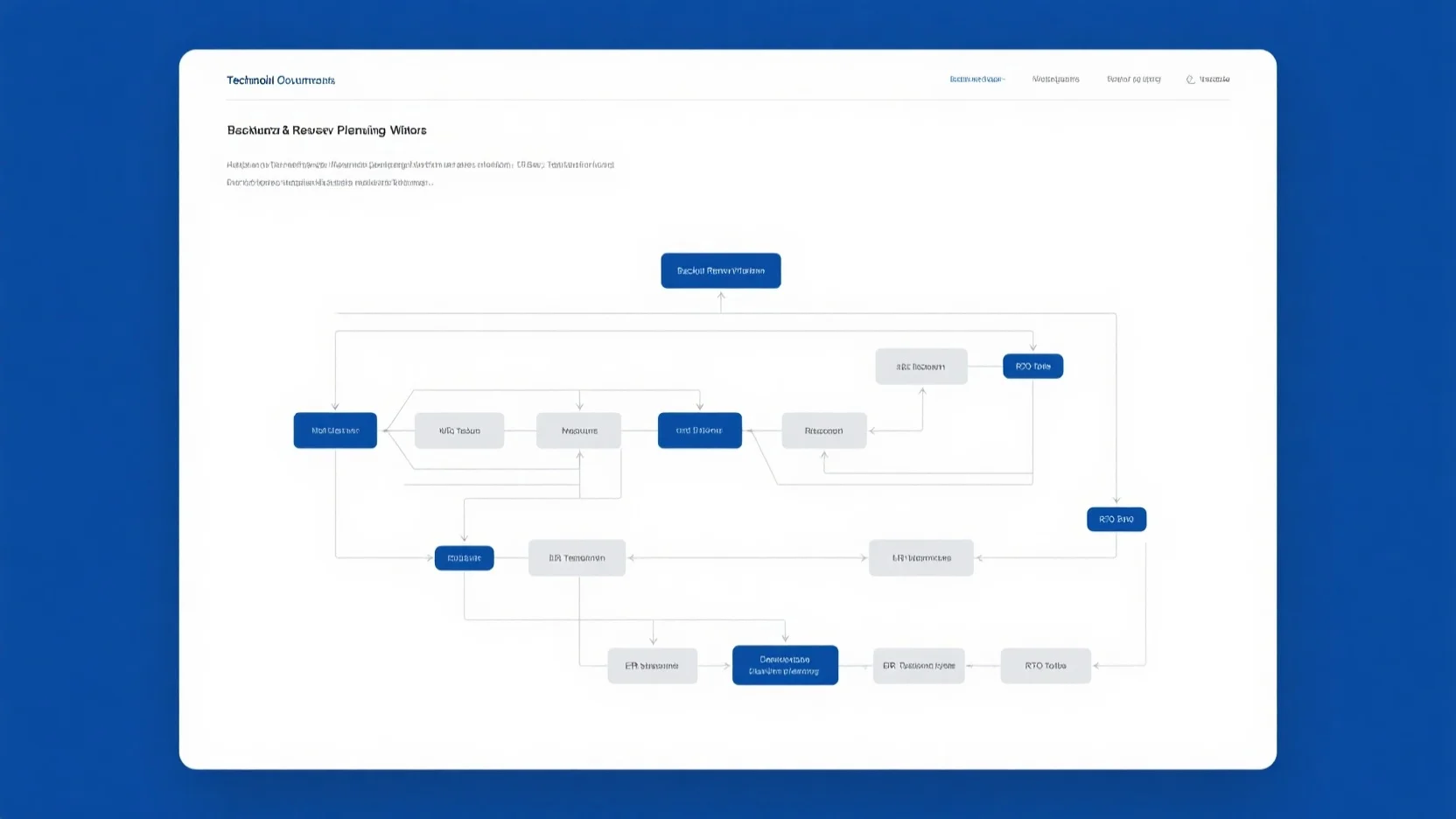
First, conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) to assess disruption consequences. Then, identify critical business processes and services. After that, assign RTO and RPO values based on risk and impact analysis. As recommended by industry best – practices, involve key stakeholders. This is further explored in our [Determining acceptable RTO and RPO for different business processes] section.
Steps for conducting a DR test for an ERP system?
- Define objectives, like testing data restoration within RTO and RPO.
- Select a testing environment (production – like or separate).
- Execute the test by restoring data and ensuring system functions.
- Evaluate results against objectives.
- Document and communicate findings. Professional tools required for accurate testing can enhance the process. Detailed in our [Step – by – Step: DR Testing Process] analysis.
Traditional ERP high – availability setup vs. cloud – based ERP high – availability setup: What’s the difference?
Traditional ERP setups rely on on – premise fault – tolerance with physical servers, having high upfront costs and limited scalability. In contrast, cloud – based ERP setups operate on a service – based model, offering flexibility and scalability. Unlike traditional ERP, cloud – based systems can easily scale resources. Check our [Differences in high – availability setups between traditional and cloud – based ERP] section for more.
